| |
Bivalves - Bivalvia - hard substrates
|

Mytilus galloprovincialis, blue mussel <12 cm, attaches to underwater rocks with a bunch super-strong bissus threads, deeper it lives on soft sediments where several mussels make a bunch attaching to each other, and putting bissus into sand or silt - like roots. Mussel is cultured at marine farms where its planktonic larvae settle on the special collecting ropes
|

Mytilaster lineatus <3 cm. Attaches with bissus threads to any hard surface - stones, piers, stems of large macroalgae. Extremely endurable species, it can live inshore. These Mytilaster shells became a substrate for red algae Lithothamnion (crust) and Corallina
|
|

Ostrea edulis, edible oyster <12 cm. Their shell grow to rocks and other oysters. Black Sea oyster population is almost completely destroyed by predator Rapana venosa whelk and protozoan parasite Bonamia
|

Crassostrea gigas, giant oyster <40 cm. Pacific species, being grown at Utrish shellfish farm near Anapa, Black Sea Caucasian coast - instead of disappearing edible oyster Ostrea edulis
|
|

Pholas dactylus <5 cm. Its shell is a toothed drill for making holes in soft rocks. Many marl stones nearshore - and some washed ashore - are densely covered by Pholas holes of about 0.5cm diameter. Sphynx blennies like to occupy empty Pholas holes
|
|
Black Sea Shells on rocky beaches - Gastropods-Gastropoda
|

Patella tarentina <5 cm, limpet - snail without curls, adheres to stone surface and scrape periphyton off it. Became rare species because of Rapana pressure; the remains of Black Sea population of limpets finds refuge in narrow slits in rocks - where Rapana can't reach them. Most of the few oysters left also grow in slits
|

Gibbula divaricata <1.5 cm, most abundant gastropod stone scraper
|
|

Gibbula adriatica <1.0 cm. lives both on stones and the branches of brown macroalgae Cystoseira barbata
|

Gibbula albida <2.5 cm - no live findings during the last 5 years
|
|

Bela nebula <0.7 cm. very rare snail
|

Cerithium vulgatum <4 cm. We don't see live Cerithiums in Black Sea in last years; their shells sometimes are used as houses by Diogenes pugilator hermit crab
|
|

Cytharella costata <0.4 cm, very rare species
|

Bittium reticulatum <1.5 cm, lives on macroalgal branches scraping periphyton and dead algal cells. Kids call them "carrots"
|
|
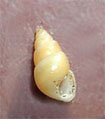
Hidrobia sp. <0.4 cm, lives on macroalgal branches
|

Nana donovani <0.7 cm, lives on macroalgal branches; kids call them "buttons"
|
|

Rissoa splendida <0.4 cm, lives on macroalgal branches
|

Tricolia pulla <0.6 cm, dominant snail species on macroalgal branches
|
|

Tritia reticulata <3 cm. Abundant detritivorous species.
Tritia shell is a favorite house of Diogenes pugilator hermit crab
|
|
Chitons

Lepidochitona cinerea <3 cm, lives on rock surfaces scraping off periphyton. Chiton shell consists of 8 overlying plates, and due to the shell flexibility this creature can roll itself into a ball. Like limpets, chitons can very strongly pull themselves to the hard surfaces. Chitons represent molluscan class separate from bivalves and gastropods. This is a picture of live Lepidochitona from the Black Sea Caucasian coast.

Teredo navalis, shipworm <25 cm, bivalvian mollusk settling in any piece of wood getting into the sea. It eats both plankton (like most bivalves), and the wood it drills. Shipworm shell is reduced to a small cap on the anterior end of the body - this small shell is its drilling tool. Teredo lines its holes in wood with a limestone stucco.
|
|

