| |
One of the youngest seas on the Earth, almost lake, the World's largest anoxic water body, draining a third of Europe, overfished and overcrowded, a model sea to study alien marine species invasions, heavily eutrophied, very beautiful, full of life: Black Sea.
Map of the Black Sea; Biodiversity, Hydrology, Geography data

Black Sea is surrounded by land, still it is not a lake since Bosporus and Dardanelles Straits connect it to the Mediterranean Sea.
Many big rivers fall into the Black Sea, making the salinity of its surface water half that of the ocean: 17‰. Reduced salinity is the cause of the relatively low biodiversity in Black Sea, since few marine species can support a viable population at salinity levels less than 20‰.
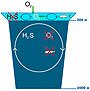 Surface water of the Black Sea is less saline and less dense, its temperature is close to that of air: warm in the summer, and very cold in the winter. This is the Black Sea familiar to most people: it is where we swim and dive, and fishermen and dolphins catch fish. Surface water of the Black Sea is less saline and less dense, its temperature is close to that of air: warm in the summer, and very cold in the winter. This is the Black Sea familiar to most people: it is where we swim and dive, and fishermen and dolphins catch fish.
Completely different is deeper Black Sea, from 50-150m intermediate layer to the very bottom at 2000 meters depth: higher salinity and density, constant temperature of 9oС.

There is very low mixing between the Black Sea surface layer and the deeper waters. That prevents penetration of oxygen to the deeper regions of the Black Sea, there is no oxygen below 200 meters. Marine animals and algae can not live in the anoxic zone of Black Sea, that water is inhabited by anaerobic bacteria which disintegrate sinking remains of the upper layer marine life. These saprophytic bacteria produce sulfuric hydride (H2S) when recycling sulfur-containing amino-acids.

The Black Sea is a young sea; it was a brackish lake some 8000 years ago, before the Bosporus breach. Today, the Black Sea ecosystem is evolving in front of our eyes: the level of the Sea rises faster than it was ever observed; human impacts on marine ecosystem such as overfishing,  over-nutrification of coastal waters, introduction of alien invasive species are changing marine life. For example, many molluscs, whose shells we still are finding on the beaches, have disappeared from Black Sea benthic habitats within recent years: they were devoured by a Pacific gastropod, Rapana venosa that colonised Black Sea in 1940s. over-nutrification of coastal waters, introduction of alien invasive species are changing marine life. For example, many molluscs, whose shells we still are finding on the beaches, have disappeared from Black Sea benthic habitats within recent years: they were devoured by a Pacific gastropod, Rapana venosa that colonised Black Sea in 1940s.

Rivers streaming into the Black Sea bring large amount of nutrients necessary for the growth of phytoplankton - invisible unicellular algae living in any drop of surface water of Black Sea. With the use of electron microscope we can discern subtle details of the smallest Black Sea creatures.
 Tiny marine plants of the Black Sea swarming in the water column are grazed on by microscopic marine animals, zooplankton: protozoans like infusoria and amoebas, small crustaceans, many other marine invertebrates and their larvae. The Black Sea plankton includes some large marine organisms, such as scyphozoan jellyfish and ctenophores. Tiny marine plants of the Black Sea swarming in the water column are grazed on by microscopic marine animals, zooplankton: protozoans like infusoria and amoebas, small crustaceans, many other marine invertebrates and their larvae. The Black Sea plankton includes some large marine organisms, such as scyphozoan jellyfish and ctenophores.

The Black Sea marine life is full of wonders, starting right at the surfline. Wading in the shallow sandy bottom we meet crabs, molluscs and benthic fish, barely discernible, always matching their color to that of bottom: gobies, flatfish, red and golden-grey mullets, stargazer, pipefish and others. A very special benthic community of the Black Sea sandy bottom is formed by the underwater meadows of Zostera seagrass.
The most diverse and interesting marine life of the Black Sea is in the rocky bottom habitats. In very shallow water, we find multicolored macroalgae, motley bright blennies, shrimps, and sea anemones.

Dense jungle of brown algae Cystoseira barbata starts at knee-depth and continues to 10-15m. Several species of wrasse live between the brown branches, and make their nests of them. Miniature marine snails slide along the algal twigs, scraping periphyton off them, little crustaceans and marine worms crawl on the thalli. Big stone  crabs, and the brightest Black Sea fish, red triplefin are hiding here. Schools of young mullets and Black Sea horse mackerels sweep over the crowns of the underwater forest. Smaller and paler Black Sea marine animals and plants need more effort to be discerned, but they are no less surprising than the big and bright ones - like almost invisible crab Macropodia longirostris growing bush of algae on its cuticle. crabs, and the brightest Black Sea fish, red triplefin are hiding here. Schools of young mullets and Black Sea horse mackerels sweep over the crowns of the underwater forest. Smaller and paler Black Sea marine animals and plants need more effort to be discerned, but they are no less surprising than the big and bright ones - like almost invisible crab Macropodia longirostris growing bush of algae on its cuticle.
 Diving deeper into Black Sea one will see blotched pickerel and damselfish schools swimming around big underwater rocks. Larger fish species are seabreams; brown meagre families hide in canyons; sea basses patrol their bottom territories. A variety of marine encrusting organisms cover rock surfaces: sponges of all colors, bryozoans, plumages of hydroid colonies, sedentary Diving deeper into Black Sea one will see blotched pickerel and damselfish schools swimming around big underwater rocks. Larger fish species are seabreams; brown meagre families hide in canyons; sea basses patrol their bottom territories. A variety of marine encrusting organisms cover rock surfaces: sponges of all colors, bryozoans, plumages of hydroid colonies, sedentary Polychaeta with flowers of gills and many other most interesting marine animals of the Black Sea. Submarine rocks end at a depth of 25-45m, and sandy shelf slopes into the darkness. It's cold here; summer thermocline in Black Sea locates at 20 to 30m. This grey plain covered with mussel shells is the home for thornback skate, Black Sea turbot, gurnard, and the small shark, dogfish. Polychaeta with flowers of gills and many other most interesting marine animals of the Black Sea. Submarine rocks end at a depth of 25-45m, and sandy shelf slopes into the darkness. It's cold here; summer thermocline in Black Sea locates at 20 to 30m. This grey plain covered with mussel shells is the home for thornback skate, Black Sea turbot, gurnard, and the small shark, dogfish.
 Marine life of the Black Sea certainly is less diverse than that of a coral reef, and the Black Sea itself is relatively small; however there are advantages to that. Marine life of the Black Sea certainly is less diverse than that of a coral reef, and the Black Sea itself is relatively small; however there are advantages to that. The Black Sea is more suitable for research, and in many ways Black Sea ecology is more comprehensible to scientists. The ecosystem of the Black Sea quickly responds to external influences, both to the natural ones, like environmental factors fluctuations, or anthropogenic effects, like fisheries, construction works in the coastal zone, and all kinds of marine pollution. The Black Sea is more suitable for research, and in many ways Black Sea ecology is more comprehensible to scientists. The ecosystem of the Black Sea quickly responds to external influences, both to the natural ones, like environmental factors fluctuations, or anthropogenic effects, like fisheries, construction works in the coastal zone, and all kinds of marine pollution.
Exploring the unusual underwater life of the Black Sea, we acquire more knowledge on the life in the Ocean.
|
|

